What Are You Looking For?
What is a Defoamer?

Defoamer refers to an agent that has chemical and interfacial chemical defoaming effect. It is a substance that can reduce the surface tension of water, solution, suspension, etc, prevent foam formation, reduce or eliminate the foam.
In the industries of textile, pulp and paper, water treatment, building materials, metal cutting liquid, agrochemical, water-based coatings and inks, oil and gas, desulfurization, fermentation,etc, a large number of foams will be produced, which will affect the product quality and production process. In order to better eliminate the foam and inhibit the formation of foam, a specific amount of antifoam is usually added to the production and processing.
Antifoam Compositions
The main components of antifoam are active ingredient, emulsifier, carrier and emulsifier additives.
Active ingredient is the most important key part, which plays the role of breaking bubbles and reducing surface tension.
Emulsifier is to disperse the active ingredient into small particles, so as to better disperse into oil or water, to play a better anti-foaming effect;
Carrier occupies a large proportion in the defoamer, and its surface tension is not high, which mainly plays the role of supporting medium and is beneficial to the effect of defoaming, and it can also reduce the cost.
Emulsifier additives are to make the emulsifying effect better.
Antifoam Characteristics
l Small dosage but strong defoaming power;
l When adding to the foaming system, it does not affect the basic properties of the system;
l Low surface tension;
l Good balance with the surface;
l Good heat resistance;
l Good diffusion and permeability;
l Chemical stability and strong oxidation resistance;
l Small solubility in foaming solution;
l High safety.
Antifoam Roles
Antifoam can be divided into three: defoamer, antifoam agent and air release agent.
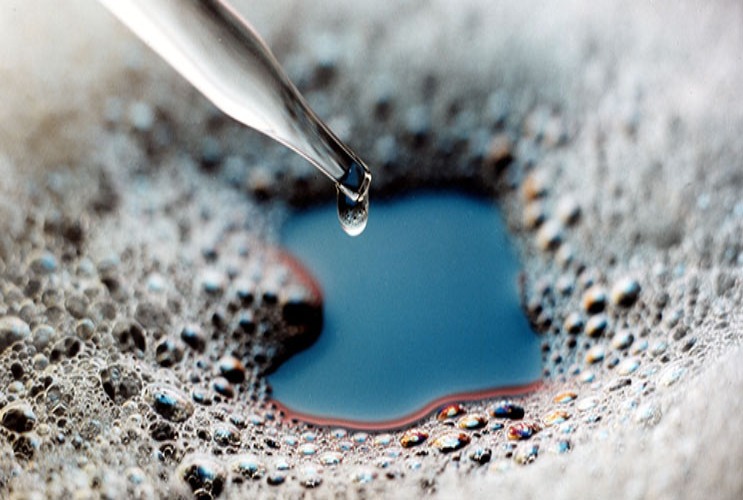

l Defoamer is added after the liquid foam system formed, and enters the bubble film through the action of foam adsorption and surface tension to make the film thinner. This quickly breaks the foam and lowers the liquid level.
l Antifoam agent is a substance that can inhibit the formation of foam, and it is adsorbed on the foam together with the liquid foam, reducing the surface tension, making the foam film thin, damaged, and preventing foam phenomenon.
l Air release agent is absorbed in the bubble of the liquid, gathering the air in the bubble. After the bubbles adsorb with each other, the adsorption interface is damaged to form a large bubble, then the buoyancy is increased, thus defoaming.
Antifoam Classification
l Form classification: solid granule, emulsion, dispersion, oil, paste, etc.
l Ingredient classification: silicone antifoam, polyether antifoam, mineral oil antifoam, fatty alcohol antifoam, powder antifoam, compound antifoam,etc.
l Industry classification: textile, pulp and paper, water treatment, building materials, metal cutting liquid, agrochemical, water-based coatings and inks, oil and gas, desulfurization, fermentation, etc.
What is foam?
Definitions of foam

Foam is a dispersion system in which gases are dispersed into liquids. Gas is a dispersing phase, and liquid is a dispersing medium. Bubbles in the liquid rise to the surface and get together.This aggregate of bubbles is called foam.
Foam itself is a thermodynamically unstable system. When the gas enters the solution containing the surfactant, it forms a foam system that is stable for a long time.
Classifications of foam
l Life of the foam: "short foam" with a life span of a few seconds and "durable foam" that can maintain a few days without breaking under the condition of no interference.
l Balance between the force of foam generation and foam breaking: "unstable foam" and "stable foam".
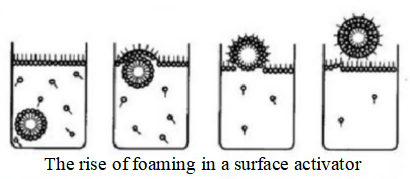
l Aggregation: "bubble dispersion system" with more liquid and less gas and "foam" with more gas and less liquid.
Decay of foam

Under the condition of gravity and pressure difference, the liquid film of the foam will flow and drain unbalanced, and the gas in the bubble will also continue to diffuse and penetrate due to the different pressure difference on both sides of the bubble film, so the instability of the foam itself is mainly reflected in the dynamics.
The attenuation mechanism mainly includes two aspects: the diffusion of gas through the liquid film and the drainage of the liquid film. Both of these properties are intrinsic to the foam itself and are independent of the presence or absence of surfactants. However, these two attenuation mechanisms are only effective in the initial stage of foam system formation. With the attenuation of the foam system, these two effects gradually weaken, making the rate of foam attenuation gradually slow down.
Methods to Eliminate Foam
(1) Physical Method
From a physical point of view, the methods of eliminating foam mainly include placing baffles or filters, mechanical stirring, static electricity, freezing, heating, steam, ray irradiation, high-speed centrifugation, pressurization and decompression, high-frequency vibration and ultrasonic waves, etc. These methods all promote the gas permeation rate at both ends of the liquid film and the liquid drainage of the bubble film, so that the number of foam gradually decreases. However, the common disadvantages of these methods are that their use is highly restricted by environmental factors and the defoaming rate is not high.
(2) Chemical Method
The methods of eliminating foam from the chemical point of view mainly include chemical reaction and adding antifoam.
The chemical reaction refers to adding some reagents to make it chemically react with the foaming agent to generate a water-insoluble substance, thereby reducing the concentration of the surfactant in the liquid film and promoting the bursting of the foam. The disadvantages are that the composition of the agent is uncertain, and the production of insoluble substances will cause harm to the system equipment.
However, nowadays, the most widely used defoaming in various industries is to add antifoam. Compared with physical methods, antifoam is easy to use and acts quickly. It only needs to add a small amount each time to achieve the ideal defoaming effect, and it also has an inhibitory effect on the formation of foam. The biggest advantage of this method is that it has high foam-breaking efficiency and is easy to use.
Working Principles of Antifoam
Principle One
Foam is a dispersion system in which gas is dispersed in liquid. Since the gas is insoluble in the surfactant, the foam forms a stable state. After the foam is formed, due to the interaction between the molecules of the foaming system, the hydrophilic group and the hydrophobic group are adsorbed by the bubble wall to form a regular arrangement. Its hydrophilic group faces the water phase, and its hydrophobic group faces into the bubble, thus forming an elastic film on the bubble interface. Its stability is very strong, and it is not easy to break under normal conditions. At the same time, the foam is a thermodynamically unstable system, and under the action of gravity, the liquid film is continuously flowing down, evaporating, and breaking, as well as the drainage and penetration between the foam liquid films.
The reasons for defoaming are mainly divided into two aspects:
(1) Defoamer molecules that are easy to spread and adsorb replace the foaming agent molecules, forming a film with poor strength;
(2) During the spreading process, the defoamer molecules take away part of the solution adjacent to the surface layer, thinning the foam liquid film and reducing the stability of the foam, so that the foam is destroyed.
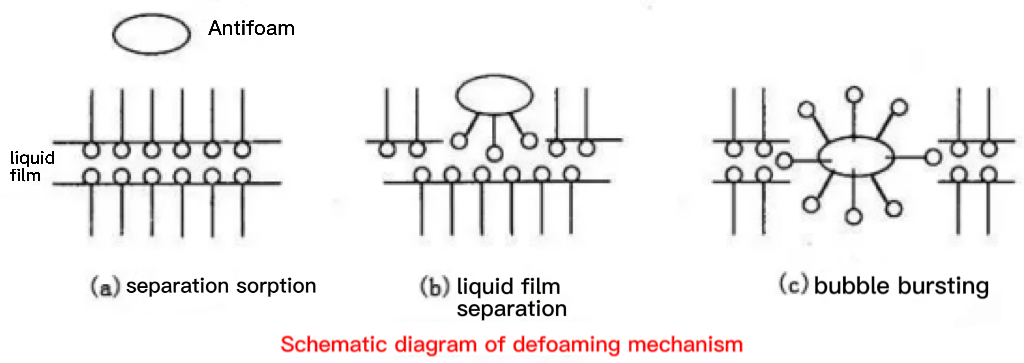
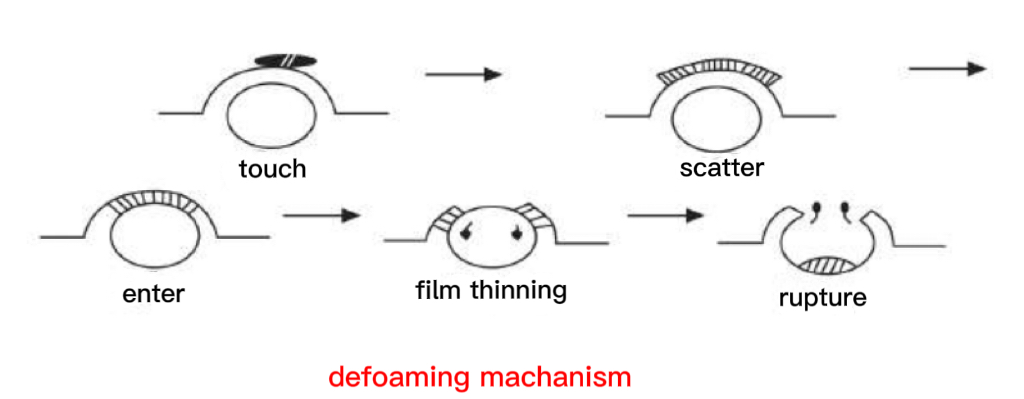
Principle Two
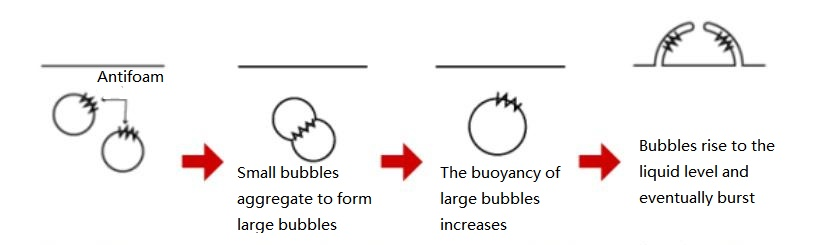
The existence of foam in the liquid is caused by the adsorption of surfactant on the gas surface, which leads to the formation of energy stable system. The principle of antifoaming agent is to change the distribution of surfactant on the surface of some bubbles, thus changing the surface tension and causing the internal pressure of these bubbles to change, and merge into other bubbles to form larger bubbles, then causing new imbalance and new merger. These large merged bubbles are eventually pushed out of the liquid by buoyance, this process called defoaming. Under the action of gravity, the bubble film will gradually thin and finally rupture, and the role of antifoaming agent is to accelerate the thinning and rupture process.
Are You Looking For Anti Foam Manufacturer ? Do You Meet the Foam Challenge ?
Antifoam company is a growth oriented, diversified, defoamer chemicals manufacturer dedicated to innovative foam control solutions in a broad range of markets.
Our total production capacity is 30000 tons+/year to ensure fast supply;
With years of experience, we have been extended protfoliio of defoamers and antifoams, including silicone defoamer, polyether defoamer, fatty alcohol defoamer, mineral oil defoamer powder defoamer and defoamer compound.
No matter what foam challenges facing you, it will be analysed and supported by our professional technical team, advanced equipments and innovated technical analysis.
For more information: Download Antifoam Brochure